Heat-Resistant Shielded Cable Benefits Ensuring Safety and Reliability in Demanding Environments
Introduction: In today's technologically advanced world, the demand for electricity and data transmission is ever-increasing. From industrial settings to residential buildings, the need for efficient and reliable power and data transmission systems is paramount. However, there are numerous challenges that these systems face, such as high temperatures, electromagnetic interference, and exposure to harsh environments. To overcome these challenges, heat-resistant shielded cables have emerged as a solution, offering numerous benefits in terms of safety, reliability, and performance. In this article, we will explore the advantages of heat-resistant shielded cables and understand why they are essential in demanding environments. 1. Understanding Heat-Resistant Shielded Cables: Heat-resistant shielded cables are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and provide reliable power and data transmission in demanding environments. These cables are constructed using specialized materials and design techniques that enable them to operate effectively even in high-temperature conditions. The primary components of a heat-resistant shielded cable include the conductor, insulation, shielding, and jacketing. Conductor: The conductor is the core component of the cable that carries the electrical current. Heat-resistant shielded cables often use materials such as copper or aluminum, known for their excellent conductivity and thermal stability. Insulation: The insulation layer surrounds the conductor, providing electrical insulation and protecting it from external factors. Heat-resistant cables use specialized insulation materials that can withstand higher temperatures than standard cables. Common insulation materials include silicone rubber, fluoropolymers, and thermoplastic materials. Shielding: The shielding layer surrounds the insulation and offers protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). Heat-resistant shielded cables typically employ shielding techniques such as braided shields or foil shields, which help minimize signal degradation caused by external electrical noise. Jacketing: The outermost layer of the cable, known as the jacket, provides additional protection against physical damage, moisture, and chemicals. Heat-resistant cables often feature jackets made of materials like polyethylene, polyurethane, or fluoropolymers, which offer excellent resistance to high temperatures and harsh environments. 2. Benefits of Heat-Resistant Shielded Cables: 2.1. Withstanding High Temperatures: One of the primary advantages of heat-resistant shielded cables is their ability to operate in extreme temperature conditions. These cables are designed to withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 250°C and even higher in some cases. This high-temperature resistance ensures uninterrupted power and data transmission in applications such as industrial machinery, furnaces, ovens, and aerospace systems, where temperatures can rise significantly. 2.2. Enhanced Safety: Heat-resistant shielded cables prioritize safety by minimizing the risk of fire and electrical hazards. The specialized insulation and jacketing materials used in these cables are flame retardant, self-extinguishing, and emit low levels of smoke and toxic gases when exposed to high temperatures or fire. This feature is crucial in applications where human safety is of utmost importance, such as in public buildings, transportation systems, and critical infrastructure. 2.3. Increased Reliability: 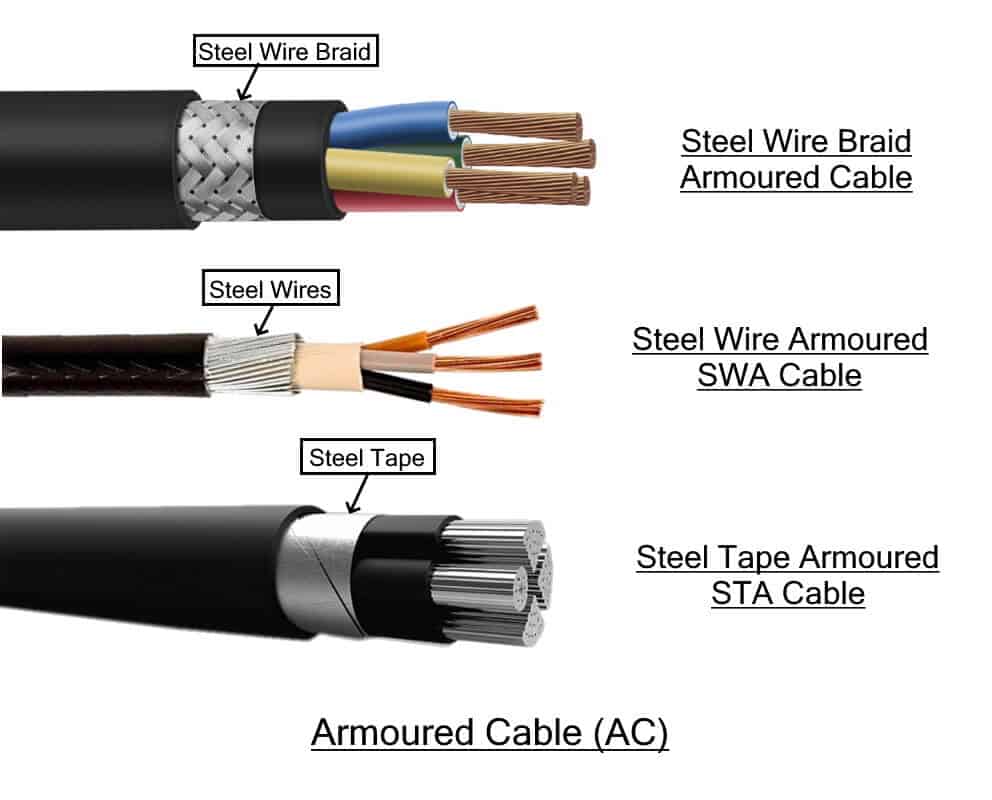 In demanding environments, where power and data transmission systems are subject to extreme temperatures, vibrations, and mechanical stresses, the reliability of cables becomes crucial. Heat-resistant shielded cables are engineered to withstand these harsh conditions, ensuring uninterrupted transmission and reducing the risk of system failures. The durable construction and advanced materials used in these cables result in a longer service life, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. 2.4. Protection against Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Radio Frequency Interference (RFI): Electromagnetic interference and radio frequency interference are common challenges faced by power and data transmission systems. EMI and RFI can degrade signal quality, leading to errors, data loss, and system malfunctions. Heat-resistant shielded cables incorporate shielding layers that effectively block external electromagnetic fields, preventing interference and maintaining signal integrity. This feature is particularly beneficial in industrial environments with high levels of electrical noise and electromagnetic radiation. 2.5. Chemical and Environmental Resistance: Heat-resistant shielded cables are designed to withstand exposure to various chemicals, oils, solvents, and other harsh substances. The specialized jacketing materials used in these cables offer excellent resistance against chemical corrosion, ensuring the cable's longevity and performance in environments such as chemical plants, oil refineries, and wastewater treatment facilities. Additionally, these cables are resistant to UV radiation, moisture, and weathering, making them suitable for outdoor applications. 2.6. Flexibility and Versatility: Despite their robust construction, heat-resistant shielded cables offer flexibility and ease of installation. They can be bent, twisted, and routed in various configurations without compromising their performance or mechanical integrity. This flexibility allows for easier installation in tight spaces and complex systems, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including robotics, automation, and control systems. 3. Applications of Heat-Resistant Shielded Cables: Heat-resistant shielded cables find applications across various industries and sectors. Some notable applications include: 3.1. Industrial Machinery and Automation: In industrial settings, where high temperatures, vibrations, and EMI are prevalent, heat-resistant shielded cables ensure reliable power and data transmission. https://www.jiangyuancables.com/the-prefad-branch-electrical-power-cable/ are widely used in machinery and automation systems, including motors, pumps, conveyors, and control panels, where precision, safety, and durability are crucial. 3.2. Aerospace and Defense: Aerospace and defense systems operate in extreme conditions, including high temperatures, pressure differentials, and electromagnetic interference. Heat-resistant shielded cables play a vital role in aircraft wiring, avionics, missile systems, and ground-based military equipment, ensuring secure and uninterrupted communication, even in challenging environments. 3.3. Energy and Power Generation: In power generation facilities such as thermal power plants, nuclear reactors, and renewable energy systems, heat-resistant shielded cables provide reliable transmission of power and control signals. These cables are designed to withstand the high temperatures generated during power generation, ensuring the safety and efficiency of the entire system. 3.4. Automotive and Transportation: Automotive and transportation systems require cables that can withstand high temperatures and provide secure data transmission. Heat-resistant shielded cables are used in electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, trains, and other transportation systems, ensuring the reliable operation of critical components such as battery systems, motors, and control units. 3.5. Oil and Gas Industry: The oil and gas industry operates in harsh environments with high temperatures, corrosive substances, and EMI. Heat-resistant shielded cables are extensively used in drilling rigs, refineries, petrochemical plants, and offshore platforms, where they provide reliable power transmission and control in critical applications. 4. Conclusion: Heat-resistant shielded cables offer numerous benefits in terms of safety, reliability, and performance, making them an essential component in demanding environments. With their ability to withstand high temperatures, protect against electromagnetic interference, and resist chemical corrosion, these cables ensure uninterrupted power and data transmission in critical applications. Whether in industrial machinery, aerospace systems, or oil refineries, heat-resistant shielded cables play a vital role in maintaining the safety and efficiency of various industries. As technology continues to advance and demands increase, these cables will continue to evolve and adapt, enabling reliable and secure connections in even the most challenging environments.
In demanding environments, where power and data transmission systems are subject to extreme temperatures, vibrations, and mechanical stresses, the reliability of cables becomes crucial. Heat-resistant shielded cables are engineered to withstand these harsh conditions, ensuring uninterrupted transmission and reducing the risk of system failures. The durable construction and advanced materials used in these cables result in a longer service life, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. 2.4. Protection against Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Radio Frequency Interference (RFI): Electromagnetic interference and radio frequency interference are common challenges faced by power and data transmission systems. EMI and RFI can degrade signal quality, leading to errors, data loss, and system malfunctions. Heat-resistant shielded cables incorporate shielding layers that effectively block external electromagnetic fields, preventing interference and maintaining signal integrity. This feature is particularly beneficial in industrial environments with high levels of electrical noise and electromagnetic radiation. 2.5. Chemical and Environmental Resistance: Heat-resistant shielded cables are designed to withstand exposure to various chemicals, oils, solvents, and other harsh substances. The specialized jacketing materials used in these cables offer excellent resistance against chemical corrosion, ensuring the cable's longevity and performance in environments such as chemical plants, oil refineries, and wastewater treatment facilities. Additionally, these cables are resistant to UV radiation, moisture, and weathering, making them suitable for outdoor applications. 2.6. Flexibility and Versatility: Despite their robust construction, heat-resistant shielded cables offer flexibility and ease of installation. They can be bent, twisted, and routed in various configurations without compromising their performance or mechanical integrity. This flexibility allows for easier installation in tight spaces and complex systems, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including robotics, automation, and control systems. 3. Applications of Heat-Resistant Shielded Cables: Heat-resistant shielded cables find applications across various industries and sectors. Some notable applications include: 3.1. Industrial Machinery and Automation: In industrial settings, where high temperatures, vibrations, and EMI are prevalent, heat-resistant shielded cables ensure reliable power and data transmission. https://www.jiangyuancables.com/the-prefad-branch-electrical-power-cable/ are widely used in machinery and automation systems, including motors, pumps, conveyors, and control panels, where precision, safety, and durability are crucial. 3.2. Aerospace and Defense: Aerospace and defense systems operate in extreme conditions, including high temperatures, pressure differentials, and electromagnetic interference. Heat-resistant shielded cables play a vital role in aircraft wiring, avionics, missile systems, and ground-based military equipment, ensuring secure and uninterrupted communication, even in challenging environments. 3.3. Energy and Power Generation: In power generation facilities such as thermal power plants, nuclear reactors, and renewable energy systems, heat-resistant shielded cables provide reliable transmission of power and control signals. These cables are designed to withstand the high temperatures generated during power generation, ensuring the safety and efficiency of the entire system. 3.4. Automotive and Transportation: Automotive and transportation systems require cables that can withstand high temperatures and provide secure data transmission. Heat-resistant shielded cables are used in electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, trains, and other transportation systems, ensuring the reliable operation of critical components such as battery systems, motors, and control units. 3.5. Oil and Gas Industry: The oil and gas industry operates in harsh environments with high temperatures, corrosive substances, and EMI. Heat-resistant shielded cables are extensively used in drilling rigs, refineries, petrochemical plants, and offshore platforms, where they provide reliable power transmission and control in critical applications. 4. Conclusion: Heat-resistant shielded cables offer numerous benefits in terms of safety, reliability, and performance, making them an essential component in demanding environments. With their ability to withstand high temperatures, protect against electromagnetic interference, and resist chemical corrosion, these cables ensure uninterrupted power and data transmission in critical applications. Whether in industrial machinery, aerospace systems, or oil refineries, heat-resistant shielded cables play a vital role in maintaining the safety and efficiency of various industries. As technology continues to advance and demands increase, these cables will continue to evolve and adapt, enabling reliable and secure connections in even the most challenging environments.